MCT oil – types of fatty acids

Division of MCT oil from a chemical point of view
MCT oil is a valuable support for the immune and digestive systems and the production of ketone bodies. It is classified as a medium-chain fatty acid, i.e. it can contain between 6 and 12 carbon atoms per molecule. In contrast to long-chain fatty acids (>12 carbon atoms per molecule), medium-chain triglycerides are easily absorbed [1]. The metabolic product of MCT oil (desirable, among other things, in ketogenic diets) are ketone bodies.
MCT fats occur naturally in many foods, including coconut oil, unrefined palm oil and dairy products. They can also be extracted as a dietary supplement – MCT oil. MCT fatty acids are divided into four types with different properties.
C6 (caproic acid or hexanoic acid)
Caproic acid (hexanoic acid) contains 6 carbon atoms in the chain. It is characterised by an unpleasant taste and odour and can also cause abdominal pain. It is found sporadically in food products. It is also not a component of MCT oils. Caprylic acid has the advantage of relatively fast digestion and energy production.
C8 (caprylic acid or octanoic acid)
C8 MCT oil, or caprylic (octanoic) acid, contains 8 carbon atoms in the chain. It is a fat with proven health-promoting benefits: it has strong antifungal and anti-inflammatory effects, supports gastrointestinal function and may also reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance. Previous research results confirm that caprylic acid can help people struggling with inflammatory bowel disease and impaired intestinal tightness. It has also been shown to be beneficial for hypertension. C8 MCT oil is considered to be of the best quality, not least because it has the highest capacity to form ketone bodies, which realistically reduces the time the body enters a state of ketosis.
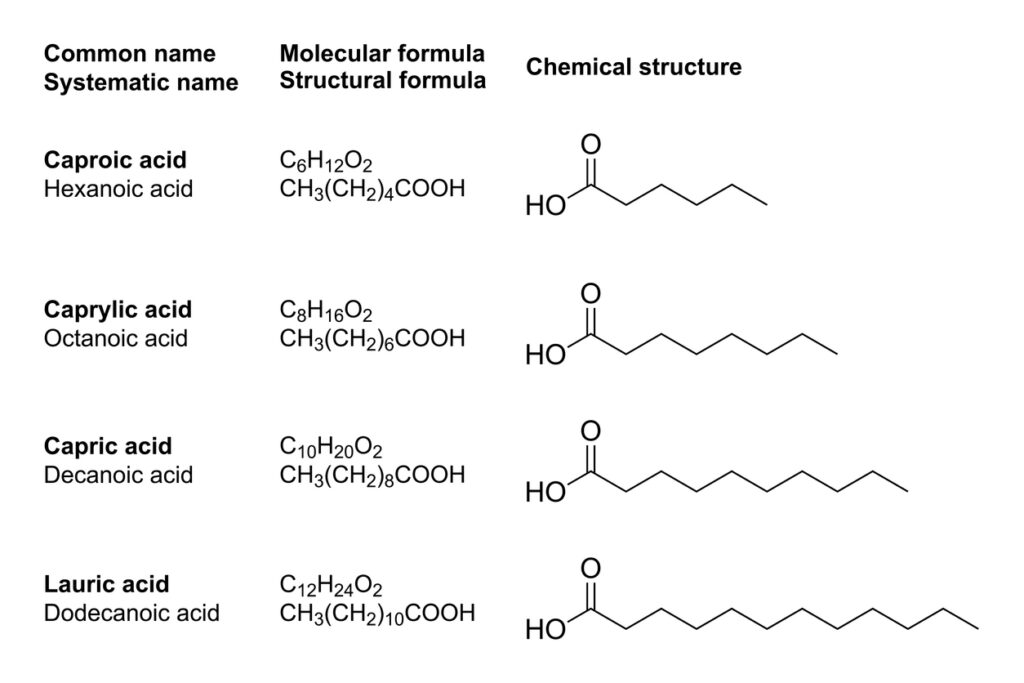
C10 (capric acid or decanoic acid)
C10 capric (decanoic) acid contains 10 carbon atoms in the chain and, like C8 acid, is widely recognised as a very good quality product. It is found in the formulation of MCT oils usually as an admixture to C8 caprylic acid. It exhibits similar but weaker antibacterial and antiviral effects. It also has an effect on increasing levels of good HDL cholesterol. C10 caprylic acid occurs naturally in breast milk, palm kernels, cow’s milk and goat’s milk, among others. It is recommended for those starting MCT oil supplementation as it is gentler on the digestive system.
C12 (lauric acid or dodecanoic acid)
C12 lauric acid contains 12 carbon atoms in the molecule. Due to its structure, it is considered closer to saturated fatty acids (LCTs). Like other MCT fatty acids, it shows health-promoting properties (mainly antibacterial), but these are negligible. Lauric acid makes up more than 50% of the composition of palm and coconut oils: for this reason, it is the main fatty acid included in the cheapest MCT oils on the market [2].
Which MCT oil is worth choosing?
C8 caprylic acid and C10 caprylic acid are considered to be the best quality MCT fatty acids, hence it is worth choosing MCT oils that include them. The benefits of supplements containing these acids are undeniable and multifaceted, so MCT oils should not be chosen at random. One should reach for products distinguished by their pure composition, free of unnecessary additives and artificial ingredients, such as MCT oil powder sourced from start to finish in accordance with the Clean Label philosophy [3]. Initially, supplementation with MCT oils may cause side effects, so it is worth introducing them gradually and starting with C10 oil.
Bibliography
[1] “Medium-chain triglycerides: an update on their metabolism and therapeutic potential in human health and disease,” Nutrition Reviews
[2] “Lauric acid: properties, production and applications”, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition
[3] “The role of medium-chain triglycerides in the promotion of health: a review of the literature,” Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology.


